The introduction of memory compression, in the realm of Windows 10, has revolutionized RAM utilization. This article delves into the essence of memory compression, elucidating its importance, and advantages, check memory compression status, and offering insights into enabling or disabling this feature.
Also Read: Let’s Solve “Windows Can’t Verify The Digital Signature for Drivers”
Decoding Memory Compression on Windows
Windows uses memory compression, dynamically shrinking data before storing it in RAM. This enhances physical memory capacity, minimizing reliance on page files and preventing slowdowns in high RAM usage scenarios. Its important advantages include:
- Optimized Memory Efficiency: Mitigates reliance on slower secondary memory, augmenting multitasking capabilities and system stability.
- Accelerated Application Performance: Facilitates swifter execution of applications by maximizing data storage in physical memory.
- Diminished Disk Utilization: Alleviates strain on storage drives, leading to more resource-efficient power consumption.
- Deferred RAM Upgrades: For average users, the optimized memory usage makes 8GB RAM a viable and efficient choice.
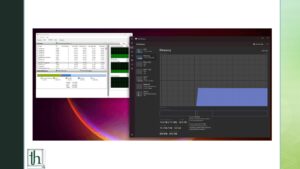
Inspect Memory Compression Status
Head to the Performance tab in Task Manager, click on Memory to check how much memory your computer is compressing in Task Manager.
Enabling Memory Compression
- Initiate PowerShell by pressing the Win key and conducting a search.
- Run PowerShell as an Administrator.
- Input the command: Enable-MMAgent -mc.
- Execute the command to activate memory compression.
Disabling Memory Compression
- Open PowerShell with Administrator privileges.
- Type the command: Disable-MMAgent -mc.
- Execute the command to deactivate memory compression.
Validating Memory Compression Status
Open PowerShell as an administrator, and input the command Get-MMAgent to check the memory compression status, i.e. whether it is enabled (True) or disabled (False).
While the option to disable memory compression exists, it is generally discouraged. The advantages it brings in optimizing RAM usage lead to smoother system performance, minimizing challenges associated with reaching full physical memory.
By comprehending the nuances of memory compression and its implications, users can make informed decisions tailored to their system requirements and personal preferences.